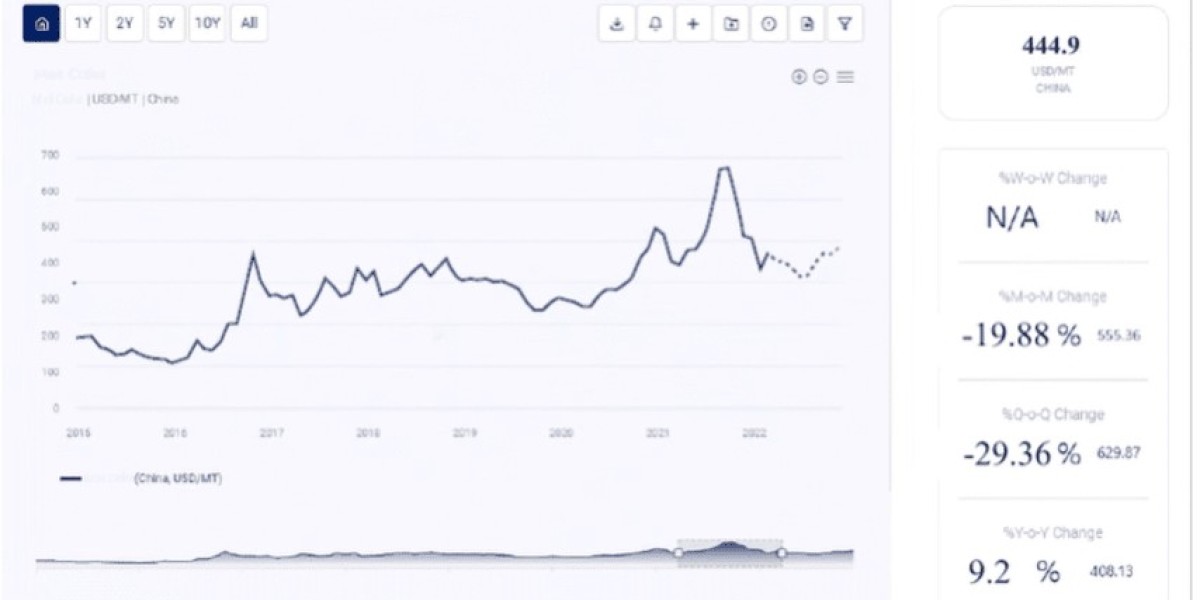
Propylene is one of the most important petrochemical feedstocks, serving as a building block for numerous downstream products such as polypropylene, acrylonitrile, and propylene oxide. Its versatile applications make it a critical material in the production of plastics, automotive components, textiles, and construction materials. However, like other petrochemicals, propylene prices are subject to significant fluctuations due to a range of market and external factors. Understanding these Propylene price trend can offer valuable insights for businesses, investors, and industry stakeholders. This article examines the key drivers influencing propylene price trends, historical patterns, and potential future outlooks.
Historical Overview of Propylene Prices
Propylene pricing has historically been closely tied to the price of crude oil and natural gas, as these are the primary feedstocks for its production. Over the decades, propylene prices have demonstrated varying degrees of volatility, influenced by macroeconomic conditions, changes in feedstock supply, and shifts in global demand.
The Oil Price Connection:
In the 1980s and 1990s, propylene prices often mirrored the price movements of crude oil. During periods of low oil prices, propylene production costs decreased, leading to lower market prices. Conversely, when crude oil prices spiked, propylene prices followed suit due to higher feedstock costs and increased production expenses.Market Diversification and Shale Gas Impact:
The emergence of shale gas in the late 2000s brought significant changes to the petrochemical landscape. In regions like North America, the increased availability of ethane-based feedstocks shifted the production of olefins, including propylene. While ethylene production benefited from cheap natural gas liquids (NGLs), propylene markets experienced tighter supply as cracking operations increasingly focused on lighter feedstocks that produced less propylene.Global Financial Crisis and Recovery:
The 2008 financial crisis caused a dramatic drop in industrial demand for propylene and its derivatives. Prices fell sharply as manufacturing activity slowed worldwide. In subsequent years, as economies recovered and industrial output rebounded, propylene prices gradually recovered as well, highlighting their close relationship to global economic health.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/propylene-price-trends/pricerequest
Factors Influencing Propylene Price Trends
Several key factors drive the fluctuations in propylene prices, ranging from feedstock availability to end-user demand. Understanding these drivers can help industry participants better anticipate market movements and adapt their strategies.
Feedstock Costs:
Propylene production relies on naphtha, propane, and other hydrocarbons as feedstocks. The cost of these raw materials directly affects production costs. For example, higher crude oil prices translate into more expensive naphtha, leading to increased propylene prices. Similarly, changes in natural gas prices can influence propane and ethane costs, indirectly impacting propylene markets.Supply and Demand Dynamics:
Global demand for polypropylene, propylene oxide, and other derivatives is a major driver of propylene prices. When demand for these downstream products surges, propylene prices often rise. Conversely, a slowdown in key industries—such as automotive, construction, or packaging—can lead to lower demand and softer prices.Refinery and Cracker Operations:
Refinery outages, maintenance shutdowns, and changes in cracking configurations can affect propylene supply. In some regions, a significant portion of propylene comes as a byproduct of gasoline production and other refinery operations. Any disruption in these processes can tighten supply and drive prices higher.Geopolitical Events and Trade Policies:
Trade restrictions, tariffs, and geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains, limiting the availability of propylene in certain regions. For example, sanctions on major exporting countries or tariffs on feedstocks can alter global trade flows, causing price volatility.Environmental and Regulatory Factors:
Stricter environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives can affect both the production and consumption of propylene. Regulations that limit emissions or encourage the use of alternative materials may reduce demand or increase production costs, influencing prices.
Recent Trends and Market Insights
In recent years, the propylene market has experienced several noteworthy developments:
COVID-19 and Market Volatility:
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on propylene prices. Early in the pandemic, demand for industrial and consumer products plummeted, causing a sharp decline in prices. However, as economies reopened and demand for packaging, medical supplies, and hygiene products surged, propylene prices rebounded. The pandemic underscored the sensitivity of propylene prices to sudden shifts in global demand.Shale Gas and the US Market:
The abundance of shale gas in the US has continued to influence the propylene market. While ethane-based production has limited propylene output, the US remains a key supplier. Changes in shale gas production levels, export capacity, and local demand have introduced a new layer of complexity to global price trends.Asia’s Growing Influence:
Asia, particularly China, has become a dominant player in the propylene market. The region’s rapid industrialisation and expansion of downstream manufacturing facilities have driven significant demand growth. As a result, price trends in Asia often set the tone for global markets. Changes in Chinese import policies, domestic production capacity, and inventory levels have a notable impact on prices worldwide.
Future Outlook for Propylene Prices
Looking ahead, several factors will shape the trajectory of propylene prices:
Energy Transition and Feedstock Shifts:
The ongoing shift toward renewable energy and more sustainable practices could influence feedstock availability. As oil and gas companies adapt to new energy realities, changes in the availability of traditional feedstocks like naphtha and propane may impact propylene production costs. In parallel, technological advancements in bio-based or renewable propylene production may introduce new pricing dynamics.Global Economic Recovery:
The pace of global economic recovery following the pandemic, along with the potential for new economic shocks, will play a critical role in propylene demand. A robust recovery in industries like automotive, construction, and consumer goods could support higher prices, while slower growth or recessionary pressures could limit price gains.Geopolitical Stability and Trade Agreements:
Ongoing trade negotiations, regional tensions, and policy changes will continue to influence propylene price trends. For instance, improved trade relations and reduced tariffs could stabilise prices, while renewed conflicts or supply chain disruptions could drive volatility.Technological Innovations and Sustainability Initiatives:
As the industry invests in more efficient production methods and seeks to lower carbon footprints, production costs may shift. Additionally, new uses for propylene or its derivatives could emerge, potentially creating new demand streams that influence future prices.
Propylene prices have always been influenced by a complex interplay of supply, demand, feedstock costs, and external factors. While historical patterns provide valuable context, ongoing developments—such as the energy transition, shifting global economic conditions, and evolving trade dynamics—will continue to shape the market. For industry stakeholders, staying attuned to these trends and understanding the underlying drivers is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities in the ever-changing propylene market.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: [email protected]
Toll-Free Numbers:
- USA & Canada: +1 307 363 1045
- UK: +44 7537171117
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA