In recent decades, the geomembrane has become a critical component in environmental protection, containment, and civil engineering projects. These flexible, impermeable membranes provide an effective barrier to prevent contaminants from leaching into soil and groundwater, making them Pulkit Plastic Products invaluable in industries such as waste management, water containment, mining, and agriculture. With their adaptability and effectiveness, geomembranes serve as essential safeguards for both the environment and public health.
This post will explore what geomembranes are, the types available, key applications, benefits, and considerations for selecting the best geomembrane for various needs. A FAQ section will answer common questions about this innovative technology.
What is a Geomembrane?
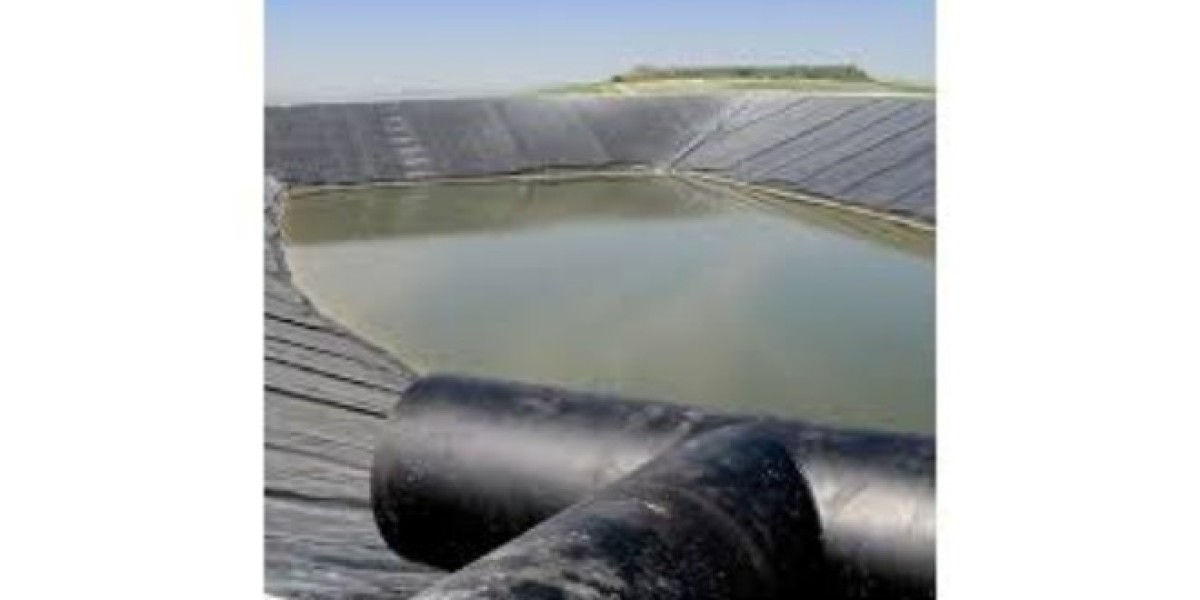
A geomembrane is a synthetic membrane liner or barrier with low permeability, used in conjunction with geotechnical engineering projects to control fluid movement. They are made from various polymers and are typically manufactured as large rolls that can be custom-cut and installed as needed. The primary purpose of a geomembrane is to create a barrier to contain liquids, gases, or contaminants, making them crucial for environmental protection applications.
Types of Geomembranes
There are several types of geomembranes, each with distinct materials, properties, and suitability for specific projects. Here are the primary types:
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Geomembranes
- Known for their chemical resistance, HDPE Geomembrane suppliers in india are durable and long-lasting. They are often used in landfill liners and mining operations due to their strength and resistance to UV radiation and harsh chemicals.
LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene) Geomembranes
- LLDPE geomembranes are more flexible than HDPE options, making them easier to install in complex, irregularly-shaped areas. They are commonly used in agriculture, wastewater containment, and pond linings.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Geomembranes
- PVC geomembranes are highly flexible and are often used in situations that require ease of installation, such as temporary containment solutions or small ponds. However, they are less resistant to chemicals compared to HDPE.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) Geomembranes
- Known for their flexibility and resistance to UV degradation, EPDM geomembranes are suitable for outdoor applications, particularly in roofing and decorative ponds. Their elasticity makes them a top choice for cold-weather installations.
Bituminous Geomembranes (BGM)
- Bituminous geomembranes are excellent for hydraulic applications, like canals and reservoirs. They are durable, self-sealing, and resist punctures well, making them ideal for environments where high durability is necessary.
Key Applications of Geomembranes
Geomembranes play a significant role across various industries and projects. Here are some of their primary applications:
Landfill Liners and Covers
- Geomembranes are used as liners in landfills to prevent leachate—contaminated water produced by decomposing waste—from polluting the surrounding soil and groundwater. They are also used as landfill covers to reduce odors, minimize rainwater infiltration, and control emissions.
Water Containment
- In applications like reservoirs, ponds, and canals, Geomembrane price in india act as a waterproof barrier, ensuring that stored water remains contained. They are also essential in agricultural ponds and aquaculture to retain water and prevent seepage into the ground.
Mining Operations
- Geomembranes are crucial in the mining industry for tailings storage facilities and heap leaching pads. By acting as a barrier, they prevent toxic chemicals and metals from leaching into the surrounding environment.
Wastewater Treatment
- In wastewater treatment plants, geomembranes are used to line lagoons and basins, preventing contaminants from escaping and protecting the surrounding land.
Oil and Gas
- Geomembranes are used as secondary containment liners in oil and gas fields to prevent oil spills and leaks from contaminating the environment.
Benefits of Using Geomembranes
Geomembranes offer numerous advantages, making them an optimal choice for containment and environmental protection:
High Chemical Resistance
- Many geomembranes, especially those made of HDPE, are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, allowing them to be used in hazardous waste containment, mining, and chemical processing.
Durability and Longevity
- Geomembranes are designed to withstand environmental stressors like UV radiation, temperature changes, and chemical exposure, making them long-lasting solutions for environmental containment.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Despite the upfront installation cost, geomembranes can save money in the long run by preventing costly environmental cleanups and reducing water loss in containment structures.
Versatility
- Geomembranes are highly versatile, adaptable to various environments, and easily customizable to fit specific project requirements, such as pond shapes or containment sizes.
Environmental Protection
- By preventing leaks and containing harmful substances, geomembranes play a vital role in protecting soil and water resources, promoting sustainable practices across industries.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Geomembrane
Selecting the right geomembrane for a project involves evaluating factors like:
Material Compatibility
- Consider the type of substances the geomembrane will contain to ensure chemical compatibility. HDPE, for example, is ideal for aggressive chemical environments, while LLDPE may be more suitable for flexible installations.
Thickness and Strength
- The geomembrane’s thickness determines its durability and puncture resistance. Projects with heavy loads or rough surfaces may require thicker materials.
Temperature and Weather Resistance
- Choose a geomembrane that can withstand the specific environmental conditions of the project location, such as UV radiation, freeze-thaw cycles, and high temperatures.
Project Longevity
- For long-term applications, HDPE or EPDM geomembranes may be preferred due to their high durability. For short-term projects, PVC may be a more cost-effective solution.
Installation Requirements
- The ease of installation varies with geomembrane types. For complex installations, LLDPE or EPDM geomembranes may be more manageable due to their flexibility.
Conclusion
Geomembranes have emerged as essential tools in industries requiring secure containment solutions. With options tailored for various applications, Geotextiles and geomembranes support sustainable practices, protect the environment, and provide cost-effective solutions for waste, water, and resource management. By choosing the right geomembrane material and considering project-specific factors, industries can benefit from reliable containment and long-term protection for their environmental projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the typical lifespan of a geomembrane?
The lifespan of a geomembrane depends on the material, installation quality, and environmental exposure. HDPE geomembranes can last over 30 years, while PVC geomembranes, typically used for temporary applications, may last 10-20 years.
2. Can geomembranes be repaired if they are damaged?
Yes, geomembranes can often be repaired using patch kits designed for specific materials. Small punctures or tears can be sealed on-site, but larger damage may require professional repair services.
3. How is a geomembrane installed?
Geomembrane installation involves site preparation, roll deployment, seam welding, and quality inspection. The membrane rolls are unrolled, joined through welding or adhesives, and then tested for leaks to ensure containment integrity.
4. Are geomembranes eco-friendly?
Yes, geomembranes are eco-friendly in that they prevent environmental contamination and groundwater pollution. They help contain hazardous materials, protecting soil and water resources and reducing the risk of long-term environmental damage.