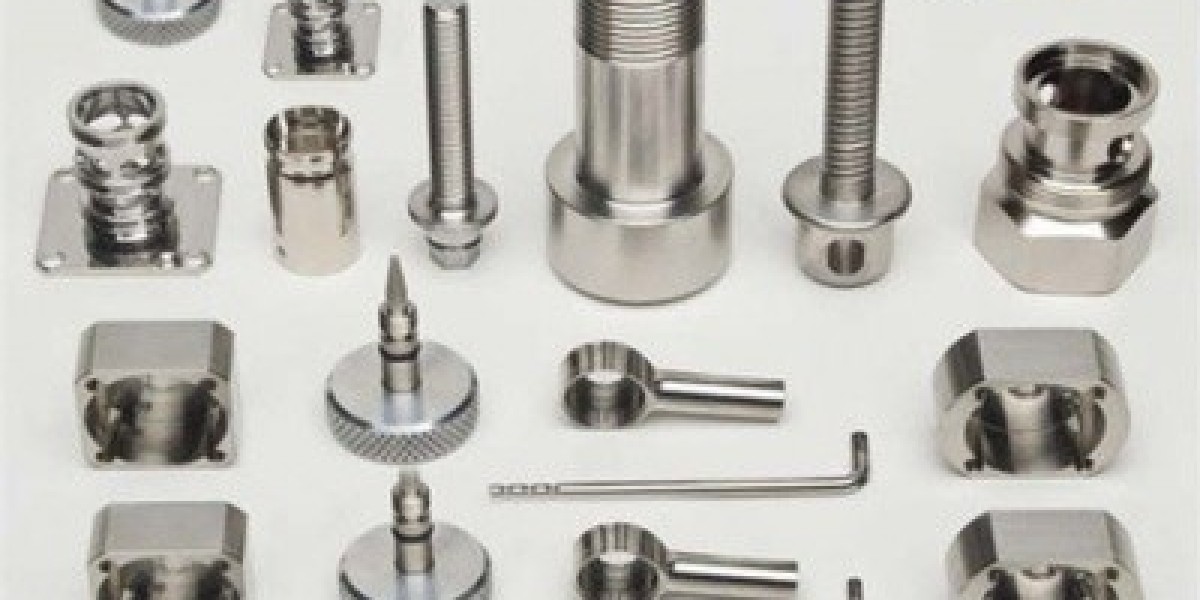
brass turned parts are precision-engineered components crafted from brass through a turning process, typically on a CNC lathe. Known for its excellent machinability, durability, and aesthetic appeal, brass is a popular material choice for a wide range of applications. Brass turned parts are utilized in various industries, including plumbing, electrical, automotive, and decorative applications, where both functionality and appearance are important.
What Are Brass Turned Parts?
Brass turned parts are components produced by machining brass billets or bars on a lathe. The turning process involves rotating the brass workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to achieve the desired shape, size, and features. Brass’s unique properties, including its machinability and corrosion resistance, make it an ideal material for precision components used in demanding applications.
Properties of Brass
Machinability:
- Brass is highly machinable compared to many other metals. It can be easily cut, drilled, and turned, making it an ideal material for producing complex and precise parts.
Corrosion Resistance:
- Brass exhibits good resistance to corrosion, especially in environments where moisture and air are present. This makes brass turned parts suitable for applications in plumbing, marine, and outdoor settings.
Strength and Durability:
- While not as strong as some other metals, brass offers sufficient strength and durability for many applications. It is often used in parts that require moderate strength and wear resistance.
Aesthetic Appeal:
- Brass has a distinct golden color and can be polished to a high shine. This aesthetic quality makes it a popular choice for decorative and high-visibility components.
Ductility:
- Brass is relatively ductile, meaning it can be deformed without breaking. This property allows for the production of parts with complex shapes and fine details.
Conductivity:
- Brass is a good conductor of electricity, making it useful for electrical connectors and components that require efficient electrical conductivity.
Common Applications of Brass Turned Parts
Plumbing:
- Brass is widely used in plumbing fixtures and fittings, such as valves, faucets, and connectors. Its corrosion resistance and durability make it suitable for water and gas applications.
Electrical:
- In the electrical industry, brass turned parts are used for connectors, terminals, and contact points. The material’s good electrical conductivity ensures efficient transmission of electricity.
Automotive:
- Brass turned parts are found in automotive components such as fittings, connectors, and fasteners. Brass’s strength and machinability make it a reliable choice for these applications.
Decorative Items:
- Brass’s aesthetic qualities make it a popular choice for decorative items such as handles, knobs, and ornaments. The material can be polished to a high shine, adding a touch of elegance to various products.
Aerospace:
- In aerospace applications, brass turned parts are used for components that require moderate strength and corrosion resistance, including fasteners and structural elements.
Lock Mechanisms:
- Brass is often used in the production of lock components such as cylinders, keys, and levers. The material’s durability and resistance to wear make it suitable for security applications.
Advantages of Brass Turned Parts
High Machinability:
- Brass’s excellent machinability allows for precise manufacturing of intricate parts with tight tolerances. This leads to high-quality finished products with minimal defects.
Corrosion Resistance:
- Brass’s resistance to corrosion ensures that turned parts maintain their functionality and appearance over time, even in challenging environments.
Aesthetic Quality:
- The natural golden color and ability to achieve a polished finish make brass turned parts visually appealing, suitable for applications where appearance is important.
Good Electrical Conductivity:
- Brass’s conductivity makes it a preferred material for electrical components, ensuring reliable performance in electrical connections and circuits.
Durability:
- Brass provides a good balance of strength and ductility, making it durable enough for a wide range of applications while remaining easy to machine.
Versatility:
- Brass can be used in a variety of applications, from functional components to decorative items, making it a versatile choice for manufacturers.
Turning Processes for Brass Parts
CNC Turning:
- CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning machines are commonly used to produce brass parts with high precision and repeatability. CNC turning allows for complex geometries and tight tolerances, essential for high-quality brass components.
Manual Turning:
- While less common for high-volume production, manual lathes can still be used for custom or low-volume brass parts. Manual turning offers flexibility for unique designs and prototypes.
Threading:
- Threading is often required for brass parts used in fittings, connectors, and fasteners. The process involves cutting helical grooves into the part to create threads for mating with other components.
Facing and Boring:
- Facing creates flat surfaces on brass parts, while boring enlarges existing holes. These processes are essential for achieving precise dimensions and finishes on components like bushings and housings.
Knurling:
- Knurling creates textured patterns on the surface of brass parts, which can improve grip or provide a decorative touch. This is commonly used for knobs, handles, and other user-facing components.
Considerations for Brass Turned Parts Manufacturing
Material Selection:
- Choose the appropriate brass alloy based on the application’s requirements. Common brass alloys include leaded brass (for improved machinability) and dezincification-resistant brass (for corrosion resistance).
Tolerances and Specifications:
- Ensure that the manufacturer can achieve the required tolerances and specifications for your brass parts. Precision in turning is crucial for parts used in high-accuracy applications.
Surface Finish:
- Decide on the desired surface finish for the brass parts. Options range from polished and shiny to matte or brushed, depending on the application and aesthetic requirements.
Quality Control:
- Verify that the manufacturer has robust quality control measures in place to ensure that brass parts meet industry standards and customer specifications.
Cost and Lead Time:
- Consider the cost and lead time for production. While brass is generally cost-effective, factors such as complexity and volume can impact the overall cost and delivery schedule.
Conclusion
Brass turned parts offer a combination of machinability, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. Whether for plumbing fittings, electrical components, automotive parts, or decorative items, brass’s unique properties and versatility make it a preferred material choice. By working with experienced manufacturers and understanding the specific requirements of your application, you can ensure the production of high-quality brass turned parts that meet your needs and expectations.