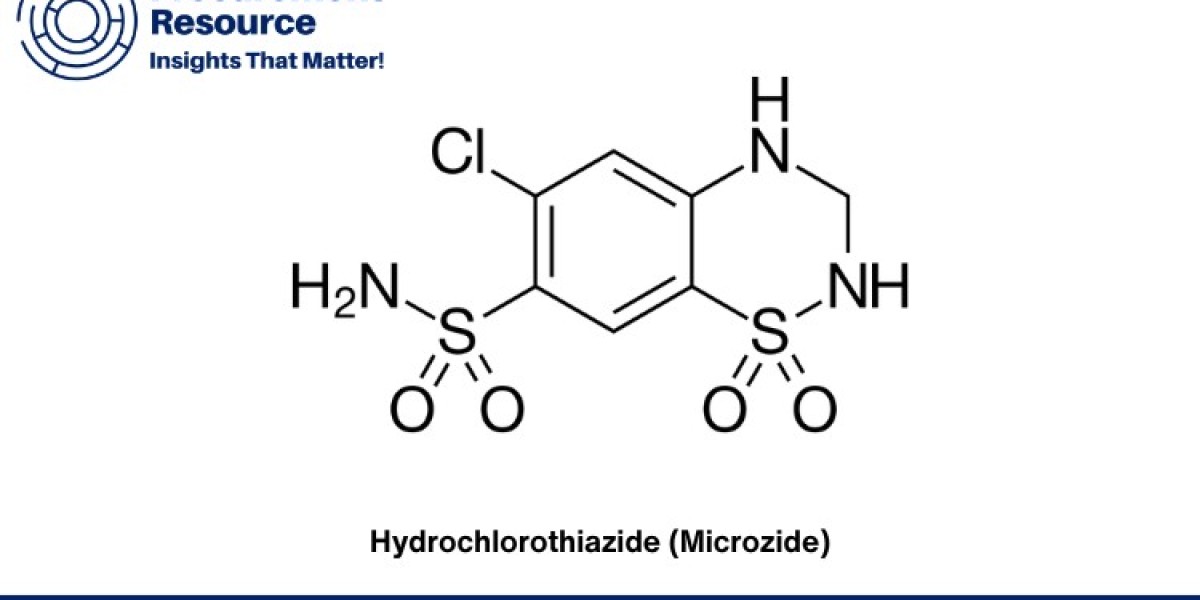
Hydrochlorothiazide, marketed under the brand name Microzide among others, is a widely used diuretic medication prescribed for conditions such as high blood pressure and edema. In this report, we delve into the production process of Hydrochlorothiazide, detailing manufacturing techniques, raw material costs, and the latest developments in its production.
Introduction of Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) Production Process
Hydrochlorothiazide belongs to the thiazide diuretic class of medications, primarily used to treat hypertension and fluid retention. Its production process involves several key steps to ensure purity, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness. The primary synthesis of Hydrochlorothiazide typically begins with the reaction between 4-amino-6-chloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide and chlorosulfonic acid, followed by subsequent purification and crystallization steps. These processes are carefully monitored to maintain high product quality and yield.
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/hydrochlorothiazide/request-sample
Manufacturing Report and Process
The manufacturing of Hydrochlorothiazide is conducted under stringent quality control measures to meet regulatory standards and ensure safety for consumer use. The process starts with the procurement of raw materials, including 4-amino-6-chloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide and chlorosulfonic acid, which undergo controlled reactions in specialized reactors. This step is crucial as it determines the yield and purity of the final product. After synthesis, the compound is purified through crystallization, filtration, and drying stages to achieve pharmaceutical-grade Hydrochlorothiazide.
Once purified, the compound is formulated into dosage forms such as tablets or capsules, where it is combined with excipients to facilitate drug delivery and enhance stability. Quality assurance protocols, including analytical testing and batch validation, are integral to the manufacturing process to ensure each batch meets pharmacopeial specifications.
Raw Material Costs
The cost of raw materials significantly impacts the overall production cost of Hydrochlorothiazide. Key raw materials such as 4-amino-6-chloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide and chlorosulfonic acid are sourced globally, with prices influenced by market demand, supply chain dynamics, and regulatory compliance. Fluctuations in raw material costs can impact manufacturing economics, prompting manufacturers to explore cost-saving strategies and alternative sourcing options to maintain competitiveness.
Latest News
Recent developments in Hydrochlorothiazide production highlight advancements in process efficiency, sustainability initiatives, and regulatory updates. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on green chemistry principles to minimize environmental impact during production. Furthermore, innovations in synthesis techniques aim to enhance yield and reduce manufacturing costs, benefiting both producers and consumers.
In regulatory news, adherence to stringent pharmacopeial standards remains pivotal, with ongoing updates impacting manufacturing practices and product quality assurance. Continuous monitoring of regulatory guidelines ensures compliance and fosters trust in Hydrochlorothiazide as a safe and effective medication.
Conclusion
Hydrochlorothiazide production encompasses a complex process involving synthesis, purification, and formulation to deliver a high-quality pharmaceutical product. The manufacturing landscape continues to evolve with advancements in technology, sustainability initiatives, and regulatory compliance shaping industry practices. As demand for Hydrochlorothiazide grows globally, manufacturers remain committed to innovation and efficiency to meet market needs effectively.
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the Hydrochlorothiazide production process, emphasizing its critical components from raw material procurement to formulation and regulatory considerations. Understanding these facets is essential for stakeholders seeking insights into the production economics and strategic developments within the pharmaceutical industry.